- News class
-
Difference between ESD levels
Release time:2017-04-27 | Source:Dongguan Ciry INCHR New Material Co., Ltd | Hits:74What is the difference between ESD levels? INCHR @Anti-Static compound , Dissipative plastic compound, Conductive plastic compound?
Static Electricity
As the name implies, static electricity is electricity at rest. The electrical charge is the transference of electrons that occurs when there is sliding, rubbing, or separating of a material, which is a generator of electrostatic voltages. For example: plastics, fiber glass, rubber, textiles, ect. Under the right conditions, this induced charge can reach 30,000 to 40,000 volts.
When this happens to an insulating material, like plastic, the charge tends to remain in the localized area of contact. This electrostatic voltage may then discharge via an arc or spark when the plastic material comes in contact with a body at a sufficiently different potential, such as a person or microcircuit.
If Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) occurs to a person, the results may range anywhere from a mild to a painful shock. Extreme cases of ESD, or Arc Flash, can even result in loss of life. These types of sparks are especially dangerous in environments that may contain flammable liquids, solids or gasses, such as a hospital operating room or explosive device assembly.
Some micro-electronic parts can be destroyed or damaged by ESD as low as 20 volts. Since people are prime causes of ESD, they often cause damage to sensitive electronic parts, especially during manufacturing and assembly. The consequences of discharge through an electrical component sensitive to ESD can range from erroneous readings to permanent damage resulting in excessive equipment downtime and costly repair or total part replacement.
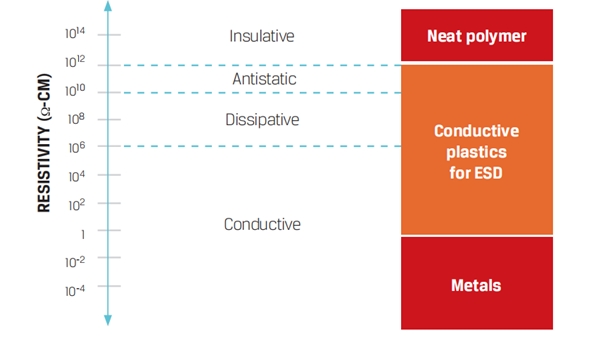
Anti-Static Grade
Preventing the buildup of static electricity. Reducing static electric charges, as on textiles, waxes, polishes, etc., by retaining enough moisture to provide electrical conduction.
INCHR@ Antistatic Plastic Compound like ESD PEEK compound contains carbon nanotube dosage level of 3-5 %wt and based peek resin to produce antistatic statically dissipative peek compounds
Resistivity of antistatic plastic compound generally between 10E+9 and 10E+11 ohms per square. Initial electrostatic charges are suppressed. May be surface resistive, surface-coated or filled throughout.
Static Dissipative Grade
The charges flow to ground more slowly and in a somewhat more controlled manner than with conductive materials. Dissipative materials have a surface resistivity equal to or greater than 1 x 10^5 Ω/sq but less than 1 x 10^12 Ω/sq.
INCHR@ Dissipative Plastic Compound contains permanent antistatic agent dosage level of 10-25 %wt and based engineering plastic material to produce statically dissipative compounds.
Resistivity of dissipative plastic compound generally between 10E+6 and 10E+9 ohms per square. Low or no initial charges -- prevents discharge to from human contact. May be either surface-coated or filled throughout.
Conductive Grade
With a low electrical resistance, electrons flow easily across the surface or through the bulk of these materials. Charges go to ground or to another conductive object that the material contacts or comes close to. Conductive materials have a surface resistivity less than 1 x 10^5 Ω/sq or a volume resistivity less than 1 x 10^4 Ω-cm.
INCHR@ Conductive Plastic Compound contains carbon nanotube,carbon fiber ,carbon powder or stainless steel fibers to produce statically dissipative compounds .
Resistivity of conductive plastic compound generally between 10E+3 and 10E+6 ohms per square. No initial charges, provides path for charge to bleed off. Usually carbon-particle or carbon-fiber filled throughout.
Pre:CHINAPLAS 2021Next:NothingRelevant information

